Did You Know?
Gout is the most common crystalline arthropathy in the United States. This condition is a multi-system disorder characterized by the inflammatory response to the deposition of uric acid (monosodium urate) in body tissues and joints. Occasionally, crystalline depositions will form into "mass-like" accumulations called "gouty tophi".
Diagnosis:
-
A gout diagnosis is often straightforward, and an aspiration of crystals from a joint or typhus will usually determine the diagnosis. However, procedures like this are invasive and always diagnostic. Inconclusive joint analyses and / or discordant serum urate levels along with atypical clinical manifestations of gout can result in delayed diagnoses and increased patient morbidity.
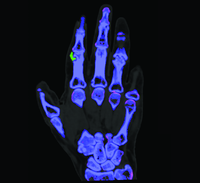
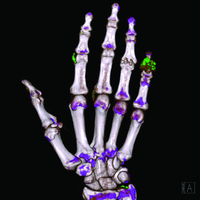
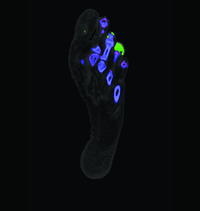
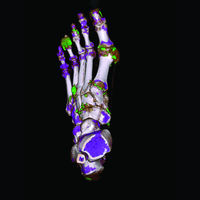
Dual Energy CT (DECT) is a new tool which can assist in equivocal cases of gout. DECT uses a special scanning technique available only on certain types of CT scanners to distinguish urate crystals found in gout from other calcific deposits.
-
Additionally, DECT can help diagnose other inflammatory arthritis which can mimic gout, including:
- Septic arthritis
- Psuedogout (CPPD disease)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
-
In patients with a confirmed diagnosis of gout, DECT technology can be used to qualify the amount of urate crystal deposition. DECT's ability to measure overall or focused tophus burden with high accuracy makes it an ideal tool to document response to therapy in daily practive or in clinical trials.
Gout Treatment Available At These Locations
Landmark Imaging Center
5510 B Presidio Parkway, Suite 2201, San Antonio, TX 78249
© 2002-2026 South Texas Radiology Imaging Centers
Material contained within this website is for informational purposes only and is not intended as professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.

